Over the past few months, I’ve been writing about the strengths and weaknesses of various large-scale paleontology exhibits from an educational standpoint. Check out the Introduction, Walk Through Time, Phylogeny, and Habitat Immersion posts if you’d like to catch up. I’ll wrap up this series for the time being with a look at two upcoming renovations of classic fossil displays, which appear to have converged on similar aesthetic, organizational, and interpretive approaches.
First up is the Peabody Museum of Natural History, where the Great Hall of Dinosaurs and adjacent Hall of Mammal Evolution have seen little modification since the 1950s. While the PMNH fossil galleries are fascinating as a time capsule of mid-century exhibit design, much of the content is rather dated and a thorough overhaul is sorely needed. PMNH staff started planning for the renovation in 2010, and I highly recommend Collections Manager Chris Norris’s blog posts on the process. Once the basic layout and concepts were in order, the museum hired the architectural firm Studio Joseph to prepare the images being used to promote the project. Fundraising is now underway, but an estimated completion date has yet to be announced.

Conceptual render of the Great Hall of Dinosaurs by Studio Joseph. Source
The big idea behind the new exhibit is the dynamic relationship between the biosphere and the Earth’s various other spheres (atmosphere, geosphere, hydrosphere, etc). The evolution of life on Earth did not occur in a vacuum, but as part of a continuously changing global system. This narrative does have a time axis – visitors will travel from the Permian at one end of the exhibit to the Quaternary at the other – but the precise divisions of geologic time are de-emphasized in favor of the broad environmental transitions that triggered evolutionary innovations. Examples might include the separation of continents during the Mesozoic, the diversification of flowering plants in the Cretaceous, or the massive climatic shift at the end of the Eocene. In this context, it’s more important that visitors understand (for example) that the Cenozoic was generally a transition from hot and wet to cold and dry (and the implications on mammalian evolution) than that they know the names and time spans of each epoch.
This approach contrasts sharply with traditional chronological exhibits, such as the Field Museum of Natural History’s “Evolving Planet.” The FMNH fossil galleries are extremely linear, and each geologic period is introduced with a set of easily-digested bullet points summarizing what happened during that time. Relatively tight spaces prevent visitors from seeing specimens from other time periods prematurely, and the galleries devoted to each period are color-coded to make them immediately distinct. According to Norris, this segmented presentation of the history of life obscures the large-scale transitions which transcend the somewhat arbitrary divisions of geologic time. As such, the new PMNH fossil halls will present the narrative holistically, encouraging visitors to track the underlying environmental trends that precipitated evolutionary change over time.

Conceptual render of the Hall of Mammals by Studio Joseph. Source
As is immediately clear from the promotional images, the new exhibit will juxtapose a modern, wide-open aesthetic with elements of the museum’s past – specifically, the outdated but gorgeous Rudolph Zallinger murals. Both of these design elements tie directly to exhibit’s narrative themes. By breaking up the central dinosaur pedestal and eliminating the unsightly glass cases in the Mammal Hall, the exhibit designers have dramatically increased the available floor space and opened up new lines of sight. This should allow visitors to view each of the galleries comprehensively, rather than as a series of discreet segments. Meanwhile, the Zallinger murals will remain a celebrated part of the exhibits. These magnificent frescoes were painted between 1942 and 1967, and are among the most iconic images of prehistoric life ever created. Although the physiology of some of the animals is outdated, Zallinger was in other ways ahead of his time. Rather than giving the geologic periods hard borders, Zallinger artfully wove the sections together so that each one fades imperceptibly into the next. The viewer can see that the flora, fauna, and climate are changing over time, but it’s a gradient, not a ladder, which perfectly reflects the narrative of the new exhibit.

A conceptual render of Deinonychus and other Cretaceous fossils. Source
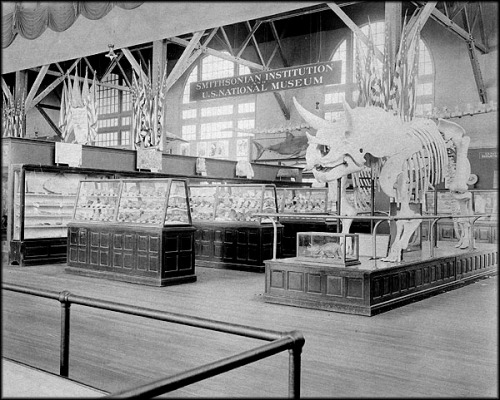
About 300 miles south of PMNH, the re-imagining of the fossil halls at the National Museum of Natural History is well underway. This building’s east wing has been home to paleontology displays since it opened in 1910 and has been updated several times, but this is the first time it has undergone a complete, wall-to-wall modernization. The old exhibits were formally closed on April 28th, 2014, and NMNH staff spent the following year removing thousands of specimens from the halls. With the fossils out of the way, the next step will be to restore the historic space to its original neoclassical glory. After that, the new exhibits and updated fossil mounts can be assembled in time for a 2019 re-opening.
Intriguingly, the planned design of the new National Fossil Hall is both thematically and aesthetically similar to the PMNH renovation, albeit on a grander scale. The National Fossil Hall’s narrative focus will be on large-scale environmental transitions over time, and how these changes drove the evolution of plants and animals. Like at PMNH, this will be accentuated by an open layout: false walls and barriers that have divided the space since the early 1960s will come down, allowing visitors to see clear across the spacious three-story hall. This airy aesthetic hearkens back to the Hall of Extinct Monsters, and like the restoration of the Zallinger murals at PMNH it represents an admirable celebration of the institution’s history.

Early conceptual render of the National Fossil Hall by Reich + Petch Source
One interpretive choice that will set the National Fossil Hall apart is the clustering of specimens on islands, or “pork chops”, as the were called early in development. Each pork chop represents North America at a particular period in time. While anchored by a few charismatic mounts, the pork chops will also include all manner of small animals, invertebrates, and plants that were part of that environment. In this way, the islands are self-contained mini exhibits, each one showing a complete ecosystem that existed at a particular time. Moving among the these displays, visitors should get a sense of how climate change and faunal interchange (among other phenomena) can completely transform an ecosystem over millions of years. They’ll also learn how certain organisms, like sauropods in the Jurassic or grass in the Neogene, can change landscapes and influence the evolution of contemporary plants and animals.
The emphasis on open spaces and freedom of movement is notable, because this is quite different from the linear exhibits of the late 20th century. In recent decades, exhibits have become increasingly structured, with specific learning goals and physical spaces designed to corral visitors through a carefully orchestrated narrative journey. Again, Evolving Planet at FMNH is an excellent example of this philosophy. The new National Fossil Hall is in some ways a push in the opposite direction – although it has a clear narrative and overarching message, visitors can roam through the exhibit as they please. I see the pork chop system as a way to have it both ways. Whether visitors work through the exhibit front to back or run straight to the T. rex in the center of the hall, then wander around at random, they’ll still be able to compare and contrast the different ecosystems and learn what the designers want them to learn.

Early concept art of the Jurassic “pork chop.” Image from The Last American Dinosaurs, NMNH.
More than anything else, what I expect to set the National Fossil Hall apart from peer exhibits will be its explicit connections to modern-day environmental crises. It’s worth quoting the Department of Paleobiology’s summary in full:
Visitors to the Museum will be able to explore how life, environments, and ecosystems have interacted to form and change our planet over billions of years. By discovering and harnessing the tools and methods paleobiologists use to study fossils, visitors will gain a deeper understanding of how the world works.
The distant past affects all of us today and will continue to do so in the future. How will climate change impact the natural world and our daily lives? How can we make informed choices about our ecosystems as individuals and as a species? How can we all become informed citizens of a changing planet?
We are in the midst of an extinction event of our own making. Anthropogenic climate change, habitat destruction, and invasive species are as dangerous as any asteroid, and will likely have profound effects on our own lives and livelihoods in the coming century. But while humans are undeniably the cause of the latest round of global changes, we also have the power to mitigate and manage their consequences. The study of fossils provides important contextual information – we can place modern organisms in an evolutionary context and understand their role in shaping the world as we know it, and we can see how organisms have responded to significant environmental overhauls in the distant past. The fossil record is in fact the only way to directly observe these things (as opposed to relying on models or actualistic experiments). As such, the new National Fossil Hall will make it clear that paleontology isn’t just about historical curiosity. The study of past life gives us a long view of the Earth’s biotic and abiotic systems, and helps us predict how they will respond to today’s environmental changes.

Concept drawing of the National Fossil Hall’s Cretaceous zone. In the old hall, the viewer would be standing at the base of the mezzanine stairs facing the rotunda. Source
With the modern climate crisis front and center, the new National Fossil Hall has the potential to be one of the most immediately relevant and important paleontology exhibits ever assembled*. This is significant, because as I lamented when I started this series, immediacy and relevance are not things that most museum visitors expect from fossil displays. While fossils, particularly the mounted skeletons of dinosaurs and other prehistoric animals, have been central to the identity of natural history museums since the late 19th century, most visitors don’t regard these exhibits as anything more than prehistoric pageantry. Visitor surveys consistently reveal that dinosaurs are seen as eye candy – monsters that might as well be from another planet. This is a shame, because dinosaurs and other prehistoric organisms were real parts of our own world, and we can learn much from them.

The new National Fossil Hall will be arranged in reverse chronological order – as visitors move accross the gallery, familiar elements of modern environments will be stripped away and the world will become an increasingly alien place. Source
And so we come full circle. What is the point of a museum exhibit**? Is it enough to provide visitors an opportunity to see cool objects and specimens? When we ask museumgoers what they want to see, they tell us “dinosaurs” or “fossils.” They don’t ask for compelling narratives or connections to big contemporary issues, and they don’t see their museum visit as an important way to bridge gaps in scientific literacy.
Still, it is of critical importance that we provide these narratives and connections. Even if we accept the fact that the very existence of a museum and the chance to see real specimens is a Good Thing, museums are still accountable to the public. Virtually all museums cite education as the primary purpose of their institution, and it’s imperative to live up to that. A museum should have a learning goal in mind, it should be able to prove that this message is coming across, and it should be able to articulate why its audience is better off for it. This is not necessarily easy – exhibits need to be relevant without being condescending or preachy. Exhibit designers need to understand their visitors as much as their content. They need to find a balance between feeding visitors information and providing a customizable experience for diverse audiences. As we have seen, not every exhibit succeeds, but my impression is that we’re getting better at it.
*It’s also notable that this climate change-focused exhibit will be on the national mall, given the ongoing politically-motivated opposition to climate science.
**Note that I’m referring specifically to public-facing exhibits. There are many good reasons why the ongoing maintenance of natural history collections is intrinsically valuable.
References
Marsh, D.E. (2014). From Extinct Monsters to Deep Time: An ethnography of fossil exhibits production at the Smithsonian’s National Museum of Natural History. http://circle.ubc.ca/handle/2429/50177
Weil, S.E. (2002). Making Musueums Matter. Washington, DC: Smithsonian Books.
Werning, S. (2013). Why Paleontology Is Relevant. The Integrative Paleontologists. http://blogs.plos.org/paleo/2013/02/19/why-paleontology-is-relevant