About 150 million years ago, a severe drought ravaged the western interior of North America. In eastern Utah, malnourished dinosaurs gathered near a dwindling river. Unwilling or unable to leave the water source, they eventually died of thirst or disease. When rain finally returned to the region, three or four successive flash floods washed dozens of animal carcasses into a relatively small depositional area to the southeast. Today, this site is known as the Carnegie Quarry at Dinosaur National Monument, and it is one of the most incredible fossil sites in the world.

Dinosaur National Monument interns collect data on the quarry wall. Source
Today, a structure encompassing a 180-foot section of the deposit (less than half its total length) allows visitors to view nearly 1400 dinosaur bones in situ. However, the fossils on display at Dinosaur National Monument represent only a portion of the material found at the Carnegie Quarry. Between the site’s discovery in 1908 and the establishment of the quarry wall exhibit, more than 20 reasonably complete dinosaur skeletons and dozens more incomplete specimens were excavated and distributed to museums in the US and Canada. No less than eleven mounted skeletons have been created from this material, and they are all still on display today. Although they are thousands of miles from their place of discovery and exhibited in four different cities, these mounts all represent individuals that lived and died in the same environment. They may have even encountered each other in life!
The Discovery
Earl Douglass was already an established fossil hunter when the Carnegie Museum of Natural History hired him in 1902. Late in the 1909 field season, Douglass was prospecting near the confluence of the Green and Yampa Rivers when he spotted a series of sauropod vertebrae eroding out of the rocks. Once Douglass and his crew began excavating the fossils, it became apparent that they had not just one remarkably complete dinosaur, but several. Douglass called it a “beautiful sight,” and CMNH director William Holland could barely contain his glee in his reports back to the Pittsburgh museum. Under Douglass’s management, CMNH crews worked at what became known as the Carnegie Quarry for 13 years. The dinosaur fossils were jumbled and often overlaid one another, so the excavators had to work on multiple skeletons simultaneously. The especially hard sandstone also slowed their work, and the team regularly resorted to huge horse-drawn plows and even dynamite to reach the fossils. Eventually railway tracks were installed to help transport blocks of sandstone out of the quarry.
In 1915, Holland successfully petitioned Woodrow Wilson to preserve the site as a national monument. CMNH crews continued to excavate until early 1923. At that point, their primary benefactor Andrew Carnegie had died, and funding for field work was dwindling. Other museums collected from the quarry periodically in the years that followed, but Douglass’s idea to contain the remaining fossils in an on-site museum was not realized until 1958.
The Mounts
Apatosaurus louisae – CM 3018
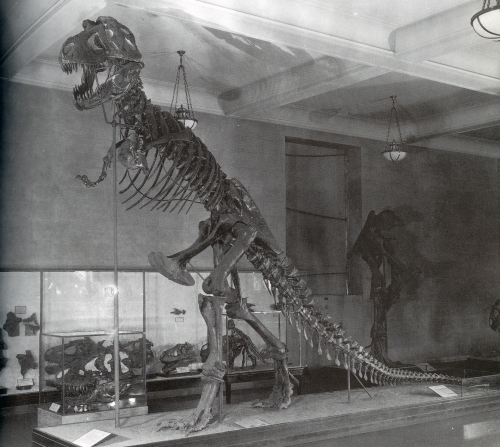
The CMNH Apatosaurus was the first dinosaur discovered at the Carnegie Quarry. After Douglass first spotted the articulated caudal vertebrae in August of 1909, his crew spent several months extracting the rest of the skeleton from the rocks. The excavation continued into early 1910, and by the time they were finished they had the most complete Apatosaurus ever found – a title the specimen holds to this day. Holland mounted the 77-foot skeleton alongside the museum’s Diplodocus in just three years, at the time a record for a sauropod mount.
Holland famously left his Apatosaurus headless for decades due to a disagreement with Henry Osborn of the American Museum of Natural History. Douglass recovered a skull that almost certainly belonged to the Apatosaurus, but Holland opted not to use it because it contradicted the sculpted head already in place on the AMNH Apatosaurus mount. After Holland’s death in 1932, museum staff quietly added a casted Camarasaurus skull as a placeholder. This was finally replaced with a proper Apatosaurus skull in 1979. More recently, the team at Phil Fraley Productions disassembled and restored the Apatosaurus, along with the rest of the classic CMNH dinosaurs. Since 2007, this specimen has been back on display in a more graceful modern pose.
Barosaurus lentus – AMNH 6341
When the CMNH team discovered this skeleton in 1912, they assumed it was yet another specimen of the well-known Diplodocus. It was harvested for parts, with portions sent to CMNH, the United States National Museum, and the University of Utah to supplement their displays. When the specimen turned out to be the more obscure sauropod Barosaurus, it languished in pieces for many years. Barnum Brown of AMNH was making a circuit of the fossil collections at various natural history museums when he rediscovered this specimen. Through a series of purchases and trades, the Barosaurus was reunited at AMNH in 1929.
Nevertheless, AMNH quickly abandoned plans to mount the Barosaurus – the museum already had a sauropod on display, and there wasn’t enough floor space for another one. It wouldn’t go on display until 1991, when Lowell Dingus conceived of the idea to mount the Barosaurus in a spectacular rearing pose as part of the renovation of the Theodore Roosevelt Rotunda. Peter May took on the project – one of the first mounts produced by his company Research Casting International. The resulting display, actually a cast, is the tallest free-standing dinosaur mount in the world.
Barosaurus lentus – ROM 3670
Douglass recovered a second partial Barosaurus skeleton in 1912, which consisted of a mostly complete torso and parts of each leg. It stayed in the CMNH collections for many years, until they traded it to the Royal Ontario Museum in 1962. ROM staff intended to mount the skeleton, but once again this was cancelled due to a lack of space. David Evans was developing a new ROM paleontology exhibit in 2007 when he learned that the museum had most of a Barosaurus sitting in its collections. With only weeks remaining before the exhibit’s opening, Evans tapped Research Casting International to mount the sauropod, supplemented with a replica neck and tail from the AMNH version.
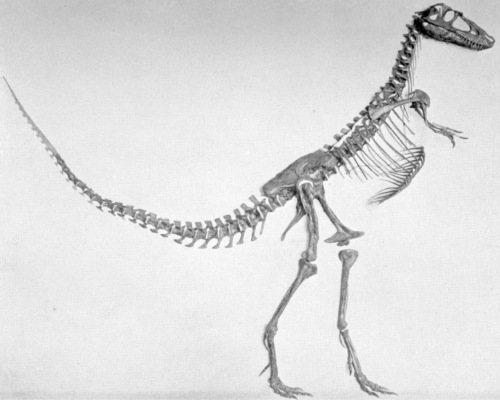
Allosaurus fragilis – CM 11844
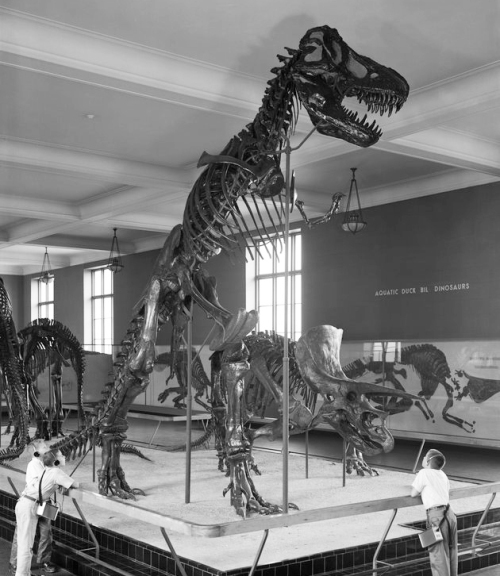
Several Allosaurus specimens are known from the Carnegie Quarry, but the one on display at CMNH is one of the largest. Douglass and his team excavated this 35-foot skeleton between 1913 and 1915. The mount was built in 1938. Although the specimen included a partial skull, the exhibit team swapped it with a cast of a more complete skull (also found in the Carnegie Quarry) from the collections of the University of Utah. This mount also includes casts of the arms of USNM 4734, an Allosaurus collected for O.C. Marsh.
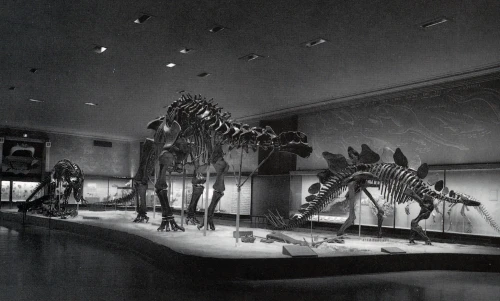
Stegosaurus ungulatus – CM 11341
The CMNH Stegosaurus is a composite of several individuals excavated from the Carnegie Quarry between 1920 and 1922. Museum staff completed the 21 foot-long mount in 1940, using a skull cast from USNM 8612. Casts of this skeleton were distributed to several other museums at some point, one of which is on display at the University of Nebraska State Museum. Phil Fraley’s company remounted the CMNH original in 2007.
Camarasaurus lentus – CM 11338
This juvenile Camarasaurus is the most complete sauropod ever found. It is displayed as a relief mount almost exactly as it was discovered, with two exceptions. The left leg was swapped with a more complete one from another individual, and the tail was re-positioned to create a more aesthetically pleasing mount. Casts of this skeleton are displayed at museums throughout the United States, including Dinosaur National Monument, but the original is at CMNH. This specimen is also notable because its left scapula is preserved in its life position, making it a helpful model for skeletal reconstructions and exhibit mounts.

NMNH Camarasaurus. Photo by the author.
Camarasaurus lentus – USNM 13786
The second best Camarasaurus also comes from Carnegie Quarry, but it is a considerably larger individual. Only the tail and a few odds and ends were missing. CMNH kept the specimen for several years before trading it to USNM in 1933 for a set of Pliocene horse skeletons. Norman Boss prepared the specimen in full view of the public during the 1936 Texas Centennial Exposition – one of the first known examples of such an exhibit. The completed mount appeared at USNM in the 1950s, sporting the tail of another Camarasaurus. At over 30 feet long, this skeleton is one of the largest dinosaurs on display at the Smithsonian. Unfortunately, the death pose somewhat limits the effect. The Camarasaurus was taken off exhibit in late 2014 for conservation and remounting. When it returns, it will be standing on its feet for the first time in 150 million years, taking its rightful place as one of the museum’s most impressive dinosaurs.
Diplodocus longus – DMNH 1494
Since this Dipldodocus was found somewhat disarticulated, Douglass suggested that the carcass may have been twisted apart while rolling downstream. AMNH held on to this skeleton for some time before trading it to the Denver Museum of Nature and Science in 1936 for two mammoth skeletons. Preparator Phillip Reinheimer mounted the skeleton with the help of 40 workers assigned to the museum through the Works Progress Administration. Additional Diplodocus fossils collected by William DeWeese (actually the first dinosaur specimens acquired by the museum) were also used to complete the mount. The Diplodocus remained on view until 1989, when Ken Carpenter and others restored and remounted the sauropod, elevating its tail and making its neck sweep gracefully to the left. The improved mount has been on display since 1995.
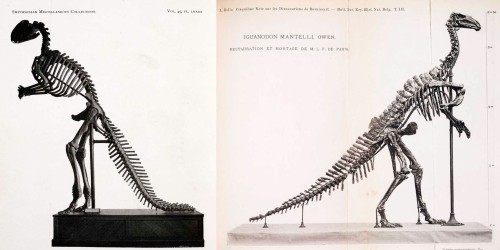
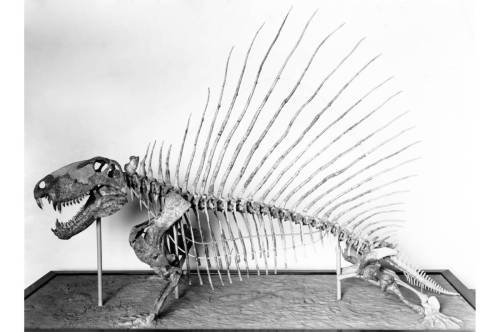
Camptosaurus aphanoecetes – CM 11337
Douglass found this controversial small ornithopod in 1922, and correctly matched it with an isolated leg several feet away. It was first identified as Camptosaurus medius, but in 2008 Ken Carpenter reassigned it to the new species C. aphanoecetes. A 2011 phylogenic study by Andrew McDonald moved this specimen to a new genus, Uteodon. Carpenter, however, asserts that McDonald’s analysis was based on an incorrectly associated Dryosaurus braincase.
CMNH staff assembled the fossils into a relief mount in 1940. The skull, hindfeet, and tail were all sculpted. During the 2007 renovation, the Phil Fraley Productions team extracted the fossils from the plaster slab, even managing to preserve the delicate ossified dorsal tendons. They then created a new, three-dimensional mount, which features a revised replica skull.

CMNH Dryosaurus. Historic photo from McGinnis 1982; modern photo by the author.
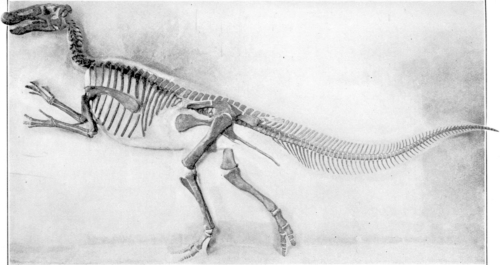
Dryosaurus altus – CM 3392
This Dryosaurus skeleton is the most complete of several collected at Dinosaur National Monument. The tail is missing, and given the completeness of the rest of the skeleton it may well have been destroyed when Douglass’s crew was blasting through rock to get to the bone layer. The Dryosaurus entered the CMNH collections in 1922, and was assembled as a 9 foot-long relief mount in 1940. In 2007, Fraley’s team removed the fossils from the plaster matrix, and just as they did with the Camptosaurus, constructed a standing mount. To date, this is the only mounted Dryosaurus specimen in the world. It is displayed alongside a juvenile Ceratosaurus cast acquired from Western Paleontological Laboratories.

NMNH Diplodocus. Photo by the author.
Diplodocus sp. – USNM 10865
The National Museum of Natural History’s Diplodocus was one of the last articulated skeletons removed from the Carnegie Quarry. When the CMNH crew closed up shop, Charles Gilmore of the Smithsonian moved in to recover one of the sauropod skeletons Douglass left behind. In 1923, Gilmore’s team excavated a partial Diplodocus, and also cherry-picked a few extra bones from an adjacent specimen. The process of mounting the skeleton at USNM took six years of continuous work, and Gilmore would later describe it as the most ambitious undertaking his department hadever attempted. The 70-foot Diplodocus mount was completed in 1931, and remained unchanged for more than 80 years. It was finally taken down in December 2014, and will return in a new pose in 2019.
Addendum: Mike Taylor recently called attention to a gorgeous map of the entire deposit prepared by Ken Carpenter, which was what prompted this post. Check it out here.
References
Carpenter, K. (2013). History, Sedimentology, and Taphonomy of the Carnegie Quarry, Dinosaur National Monument, Utah. Annals of the Carnegie Museum 81:3:153-232.
Dingus, L. (1996). Next of Kin: Great Fossils at the American Museum of Natural History. New York, NY: Rizzoli International Publications, Inc.
Gilmore, C.W. (1941). “A History of the Division of Vertebrate Paleontology in the United States National Museum.” Proceedings of the United States National Museum 90.
McGinnis, H.J. (1982). Carnegie’s Dinosaurs: A Comprehensive Guide to Dinosaur Hall at Carnegie Museum of Natural History, Carnegie Institute. Pittsburgh, PA: The Board of Trustees, Carnegie Institute.